what methods would hospitals employ to eliminate mrsa from their facilities
Name:_____________________________________ Date:____
Case Study: How Exercise Bacteria Go Resistant?

Part 1: What is MRSA?
No matter what doctors did, the babe's oxygen levels were dropping as a drug resistant leaner were eating holes in the lungs of the 7 week former. Fifty-fifty the well-nigh powerful antibiotics could not terminate the infection. Just two days agone, Madeline had started coughing, a symptom the doctor dismissed as a viral infection. And then Madeline's mother institute her limp and bluish in her crib and she was rushed to the hospital. She was diagnosed with sepsis and a virulent pneumonia that was destroying her lungs. It was MRSA.
The methicillin-resistant form of the bacterium commonly known as staph was outset identified in the 1970's in hospitals, but information technology has since spread across the world, showing up in day cares, schools and other public spaces. Today, ane.ii meg MRSA infections occur in hospitals in the U.S. and invasive MRSA kills over xix,000 per twelvemonth. The bacterium can sometimes "colonize" a person and non cause disease. The person tin can behave it on their bodies for years and pass them to other people or leave them on surfaces. Hospitals have mounted aggressive campaigns to eliminate MRSA from their facilities.
Madeline's parents wondered how she had contracted this dangerous bacterium. Madeline's family unit agreed to tests to determine if any of them were carrying the deadly bacteria or if the kid contracted the leaner from the hospital. The hospital protested, claiming that their facility is not the source of MRSA.
In the by, penicillin was used to treatStaphylococcusaureus infections. Shortly subsequently,S.aureus became resistant to penicillin. During the 1950s, derivatives of penicillin was discovered by pharmaceutical companies that could care forStaphylococcusaureus. The graph below depicts the Spread of Antibody-ResistantS.aureus Infections in the United States. Separate curves are shown for bacteria that acquired infections in the hospital ("Hospital-Acquired") and in good for you people in the customs ("Community-Acquired").
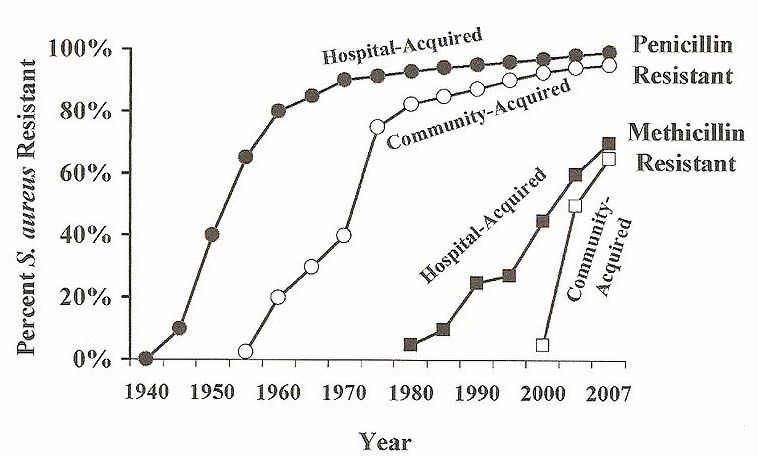
one. Based on the graph, make an inference about where the "community acquired" penicillin resistant S. aureus originated from.
two. Why did methicillin resistance lag behind penicillin resistance? Based on the trend seen with penicillin, what would you expect to encounter happen with methicillin?
Function 2: MRSA Screening
A methicillin resistantStaphylococcus aureus (MRSA) screen is a exam that looks for the presence of MRSA and no other pathogens. It is primarily used to identify the presence of MRSA in a colonized person. On a customs level, screening may be used to help determine the source of an outbreak. On a national level, boosted testing may inform clinicians and researchers about the unique genetic characteristics of the strains of MRSA circulating in the community or wellness care setting.
 A nasal swab is nerveless from the nares (nostrils) of an asymptomatic person and cultured (put onto a special nutrient medium, incubated, and then examined for the growth of characteristic MRSA colonies). A swab may exist nerveless from a wound site or skin lesion of a person who has been previously treated for a MRSA infection and cultured similarly. A screening civilisation identifies the absence or presence of MRSA and usually takes 1 to 2 days for a result.
A nasal swab is nerveless from the nares (nostrils) of an asymptomatic person and cultured (put onto a special nutrient medium, incubated, and then examined for the growth of characteristic MRSA colonies). A swab may exist nerveless from a wound site or skin lesion of a person who has been previously treated for a MRSA infection and cultured similarly. A screening civilisation identifies the absence or presence of MRSA and usually takes 1 to 2 days for a result.
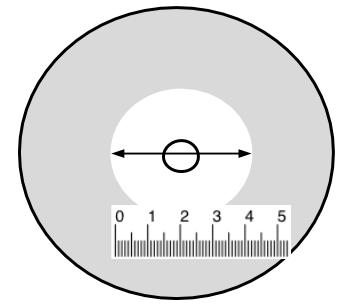
When studying how bacteria respond to antibiotics, the Kirby-Bauer disk improvidence method is used. In this technique, discs containing antibiotics are placed on agar where bacteria are growing, and the antibiotics diffuse out into the agar. If an antibiotic stops the bacteria from growing, nosotros tin see circular areas around the wafers where leaner have not grown. This area is called the "zone of inhibition." The diameter of these zones is measured equally shown below.
iii. What methods would hospitals employ to eliminate MRSA from their facilities?
4. What is a "strain" of leaner? How is is possible that some strains of Staphylococcus aureus tin can be harmless, but others tin can be deadly? (You may need to google this.)
5. A young scientist suggests that a chemical found on the skin of frogs tin be used as an antibody. Explain how the Kirby-Bauer disk technique could be used to back up this hypothesis.
6. Consider the data gathered from the frog-skin experiment. What decision would you draw from the data?
| Site | Zone of Inhibition |
| Frog Peel | 1.2 cm |
| Penicillin | 3.9 cm |
| Amoxicillin | 3.6 cm |
| Control | 0.ane cm |
Office 3: Analyzing the Plates
Each plate below represents a sample taken in the investigation. Nasal swabs were taken from private family members and two samples were taken from the infirmary delivery room. The samples were grown on agar with antibiotic disks added.
PE = penicillin | ME = methicillin | CE = cephalothin | VA = vancomycin
Measure out the zones of inhibition on the plates and record the information in the table.
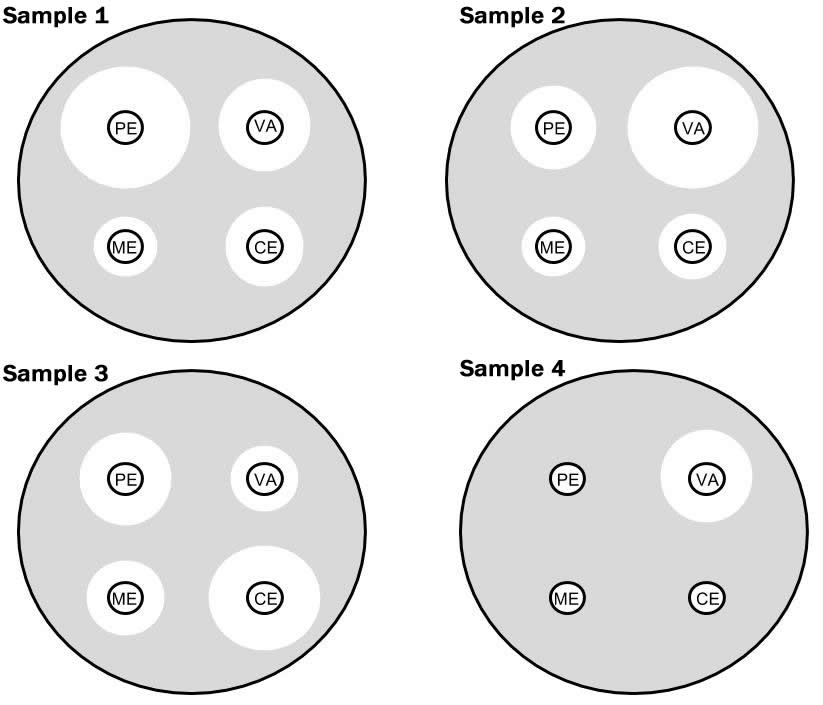
| Sample | Disk | Zone Size | Sample | Disk | Zone Size | |
| i | PE | 3 | PE | |||
| ME | ME | |||||
| CE | CE | |||||
| VA | VA | |||||
| 2 | PE | iv | PE | |||
| ME | ME | |||||
| CE | CE | |||||
| VA | VA |
Role iv: Conclusions
6. The post-obit table identifies the sample sources. Which sample contains MRSA? How practice you know?
| Sample ane | Madeline's Female parent |
| Sample 2 | Madeline's Sister |
| Sample iii | Madeline'due south Begetter |
| Sample 4 | Delivery Room Surface |
7. Sample 2 was taken from a nasal swab of a family member who has been having sinus infections. What form of antibiotics would you recommend?
eight. What recommendations would y'all make to Madeline's family and the hospital where Madeline was delivered. Your recommendations should include evidence-based reasoning and details from the case to support your position.
montgomerywhimpaincy.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.biologycorner.com/worksheets/case_study_bacteria_resistance.html
0 Response to "what methods would hospitals employ to eliminate mrsa from their facilities"
Post a Comment